Unlock the Secrets of TPU Filament: Discover Its Game-Changing Properties for 3D Printing!
TPU filament, or thermoplastic polyurethane filament, has become a go-to choice for 3D printing enthusiasts and professionals alike. Its versatility and unique properties have contributed to its rising popularity in various applications, from automotive components to custom footwear. Unlike rigid filaments, TPU offers exceptional elasticity and flexibility, allowing for the creation of parts that can withstand bending and stretching without breaking. This capability is particularly valuable in industries where durability and resilience are paramount. As more creators discover the potential of TPU filament, it is clear that its relevance in 3D printing is only set to increase.
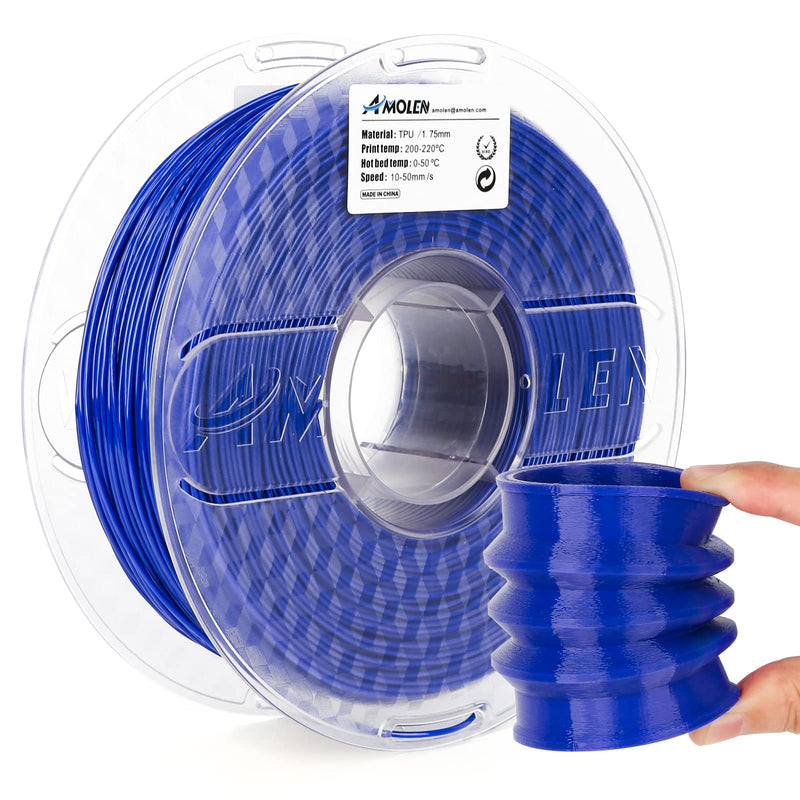

Understanding TPU Filament
TPU filament is a type of thermoplastic elastomer, meaning it combines the properties of rubber and plastic. Its chemical composition includes isocyanates and polyols, which create a flexible yet durable material. This makes TPU fundamentally different from other common 3D printing filaments like PLA or ABS, which are rigid and lack the same level of flexibility. A friend of mine, an avid 3D printing enthusiast, once shared his experience of using TPU for creating custom phone cases. He was amazed by how the material allowed for a snug fit that could easily absorb shocks from accidental drops. The elasticity of TPU makes it an ideal choice for items that require a bit of give, making it one of the most sought-after materials for functional prototypes and end-use products.
Properties of TPU Filament
The physical and mechanical properties of TPU filament are what set it apart. TPU boasts impressive tensile strength, making it resistant to wear and tear, which is crucial for parts that undergo frequent movement or stress. Its abrasion resistance helps ensure that printed pieces maintain their integrity even after extended use. Moreover, TPU has a wide temperature tolerance, allowing it to perform well in various environmental conditions. These qualities significantly affect print quality and usability; parts printed with TPU can exhibit smoother surfaces and improved durability compared to those made with more brittle materials. I remember attending a workshop where a demonstration highlighted TPU’s ability to maintain its shape and functionality after being stretched and released, showcasing its true potential. This level of resilience is essential for applications such as automotive parts, where reliability is key.
Applications of TPU in 3D Printing
TPU filament finds a multitude of applications in 3D printing, reinforcing its status as a game-changing material. In the automotive industry, for instance, TPU is used to create flexible hoses, gaskets, and seals that can withstand various stresses. In the medical field, TPU is becoming increasingly popular for fabricating prosthetics and orthopedic devices, as its flexibility allows for a more comfortable fit for patients. Additionally, consumer goods such as phone cases, footwear, and wearable technology benefit greatly from TPU’s properties. I recall a project where a friend designed a custom pair of insoles using TPU, which provided the shock absorption he needed for his active lifestyle. This versatility makes TPU an excellent choice for both functional prototypes and end-use products across various sectors.
Tips for Successful TPU 3D Printing
Printing with TPU filament can be a rewarding experience, but it does come with its challenges. To ensure successful prints, it’s crucial to adjust your printer settings appropriately. A slower print speed often yields better results, as it allows for greater precision. Additionally, bed adhesion can be tricky with flexible materials, so using a heated bed and applying a suitable adhesive can help prevent warping. Post-processing can also enhance the quality of your prints; techniques like sanding and painting can give your TPU pieces a polished finish. One common issue that newcomers face is stringing, which can be mitigated by fine-tuning retraction settings. My friend who prints with TPU often shares that patience and experimentation are key, and this advice has proven invaluable for many in the 3D printing community.
Embracing TPU in 3D Printing
In summary, TPU filament stands out as a versatile and essential material in the world of 3D printing. Its unique properties, such as elasticity and durability, make it suitable for a wide range of applications, from automotive parts to consumer goods. As we continue to explore the capabilities of TPU, it is evident that it plays a significant role in advancing 3D printing technology. Whether you are a hobbyist or a professional, embracing TPU filament in your projects can lead to innovative designs and functional prototypes. So, why not dive into the world of TPU and unlock new possibilities in your 3D printing endeavors?