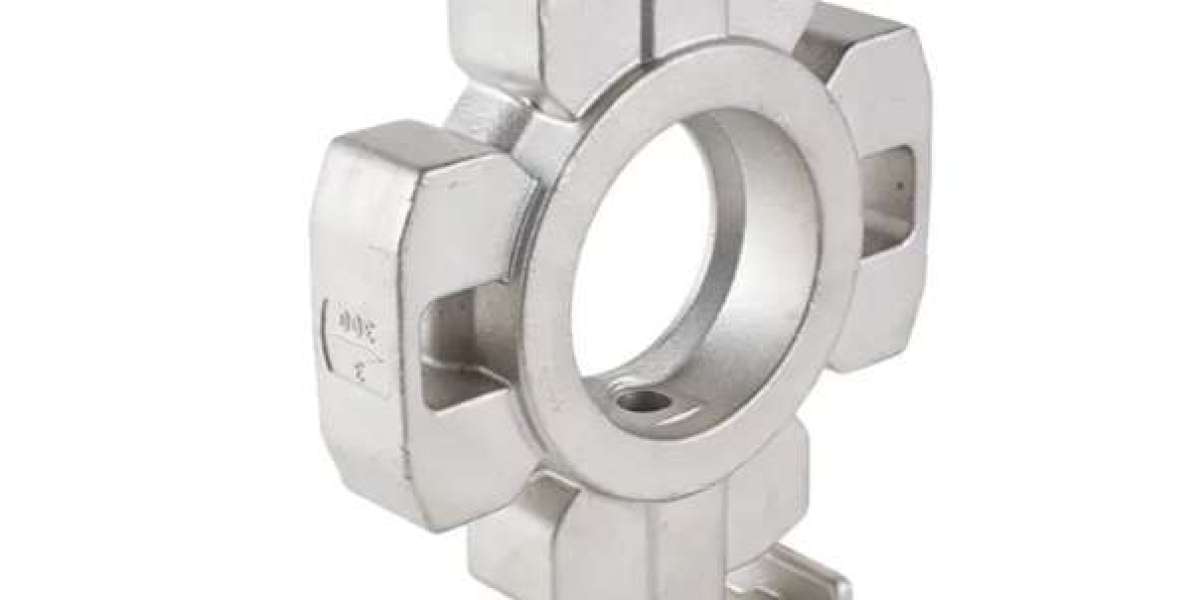
The cryogenic valve casting segment is gaining attention as liquefied natural gas (LNG) infrastructure expands globally. The term cryogenic valve casting refers to the manufacturing of valves designed to operate in ultra-low temperature environments, often for fluids like LNG, liquid nitrogen or liquid hydrogen. Such castings must deliver reliable sealing and durability in these demanding conditions. Companies that specialise in cryogenic valve casting are responding to increasing demand for flow control solutions that support the growth in LNG terminals and gas-handling systems.
One key development in cryogenic valve casting is the shift toward advanced alloys and casting methods. Traditional steels and cast iron are being replaced or supplemented by nickel-based alloys, stainless steels with special treatment and metal-to-metal sealing surfaces. These improvements reduce leakage risks and extend service life even under sub-150 °C conditions. Manufacturers of cryogenic valve castings are also applying more rigorous quality assurance, including non-destructive testing and enhanced traceability of cast components.
Regional demand is shaping the market for cryogenic valve casting. Asia-Pacific has become a core region for LNG import terminals and associated cryogenic equipment, which places pressure on local foundries and casting suppliers to meet shorter lead-times and higher certification standards. In North America and Europe, hydrogen infrastructure projects are emerging, and cryogenic valve castings must meet both temperature and pressure demands specific to hydrogen service. That means foundries engaged in cryogenic valve casting are adapting to meet diversified end-user needs.
From a business standpoint, companies offering cryogenic valve casting are benefiting from stronger service-after-sales networks and value-added offerings. For example, foundries may provide pre-machining, heat-treatment and compatibility with valve manufacturers as part of an integrated supply strategy. Such holistic support improves project delivery and adds clarity for purchasers of cast cryogenic valve components. As more industrial users emphasise reliability and life-cycle cost, the role of cryogenic valve casting stands out.
Looking ahead, the landscape for cryogenic valve casting will likely see greater use of digital tools in casting design and production, including simulation of thermal stress and fluid dynamics. Foundries that specialise in cryogenic valve casting may also deploy additive-manufacturing (3D-print) techniques for complex geometries while retaining the benefits of casting approaches.